5 Successful Products that Began as Arduino Prototypes
Since its launch in 2005, the well-known open-source electronic prototyping platform Arduino has enabled creators, hobbyists, and business owners to turn their concepts into working prototypes.
Arduino was never intended to be a new product development platform, and it was created originally for educational purposes.
But due to it’s flexibility and popularity it has grown way beyond it’s originally intended purpose, and many new product innovators use it as a prototyping platform.
In fact, there are lots of popular commercial products on the market that started as an Arduino based prototype.
In this article we’ll take a closer look at five successful products that began as an Arduino prototype, and look at some of the various challenges they ran into.
Cubetto by Primo Toys
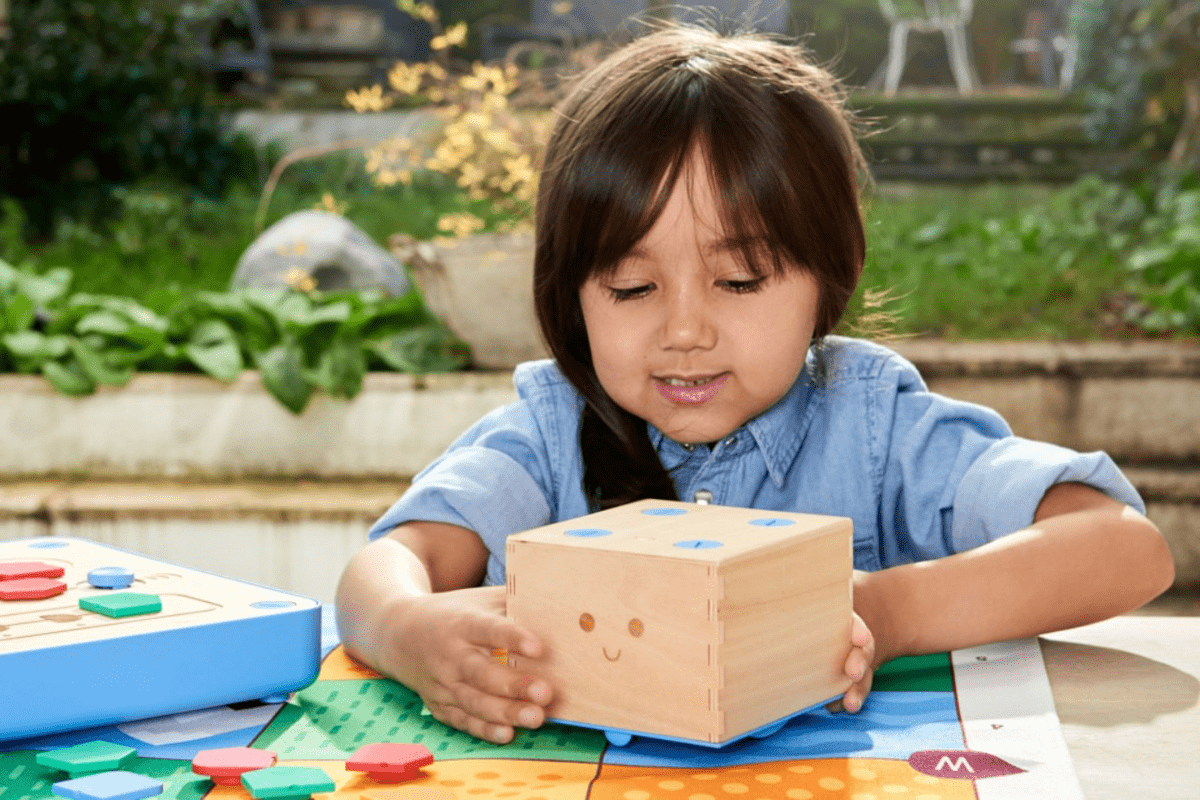

Cubetto, by Primo Toys is an educational toy designed to teach kids age 3 and up the fundamentals of coding and computational thinking, without using a screen.
They learn computing skills by interacting with Cubetto, a smiling wooden robot.
The original plan for the product was to provide a fun, tactile method of teaching coding to kids as young as three.
Cubetto’s prototypers started off using an Arduino board. They experimented with various input techniques before settling on a series of coding blocks that could be inserted in a control panel and directed the movement of the robot.
Converting the Arduino-based prototype into a reasonably priced, mass-producible, and child-safe device was one of the toughest obstacles.
The design had to be improved, the right materials had to be found, and special printed circuit boards (PCBs) had to be created to take the place of the Arduino in the finished product. Electronic products marketed for kids also have to obtain additional safety certifications.
With more than $1.6 million raised on Kickstarter, Cubetto was a spectacular success. Today, it’s sold in more than 100 countries to give children an engaging, hands-on introduction to coding.
FarmBot
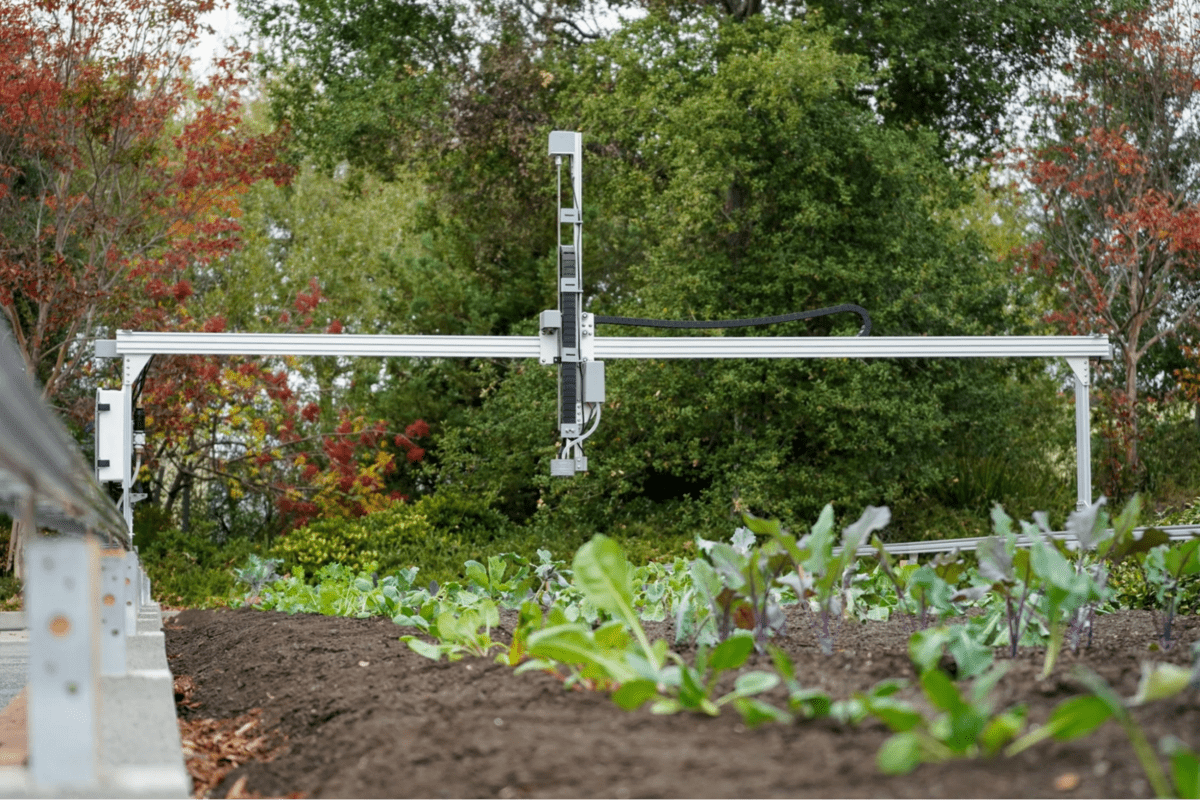

Everyone can now access small-scale, sustainable agriculture thanks to FarmBot, an automated farming system. The system can water, monitor, and plant plants, all under the direction of an easy-to-use interface.
Its robotic-like arm can also identify and pluck out weeds, effectively eliminating the need for herbicides.
During the prototyping stage, the team created a sturdy and dependable system that could survive outdoor conditions, while being controlled using an Arduino platform.
FarmBot ran a successful crowdfunding campaign, garnering more than $800,000. This enabled them to scale production by improving the product’s design, and customizing the electronics.
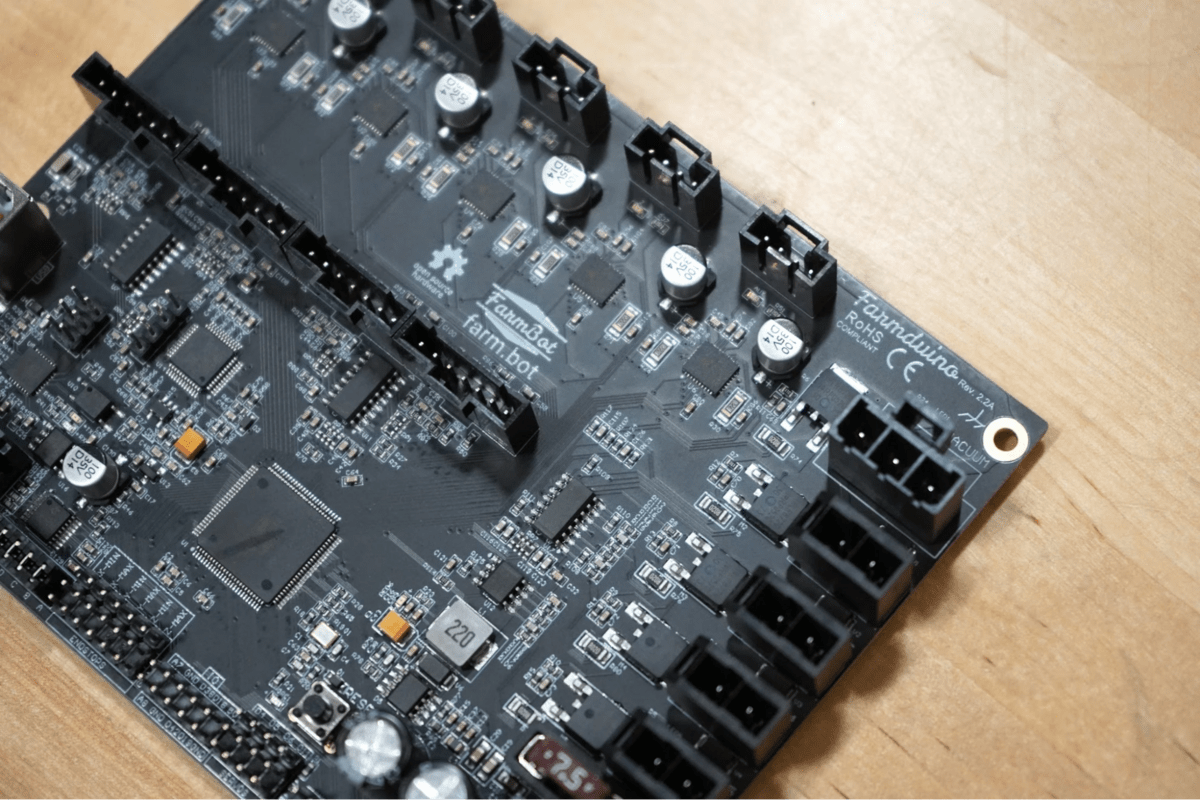
The FarmBot sold today uses a customized Arduino based PCB called the Farmduino board which has connectors and a board layout specifically for FarmBot’s many tools and functions.
It features an Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller that receives commands from a Raspberry Pi and controls various stepper motors, sensors and peripherals.
To make FarmBot’s motions quiet, it uses integrated Trinamic TMC2130 stepper drivers. It has a STM32 coprocessor that monitors the rotary encoders, and enables rapid processing of encoder signals.
Customers of FarmBot include everyone from home gardeners to educational institutions, and its open-source nature allows the technology to be adopted by anyone, anywhere.
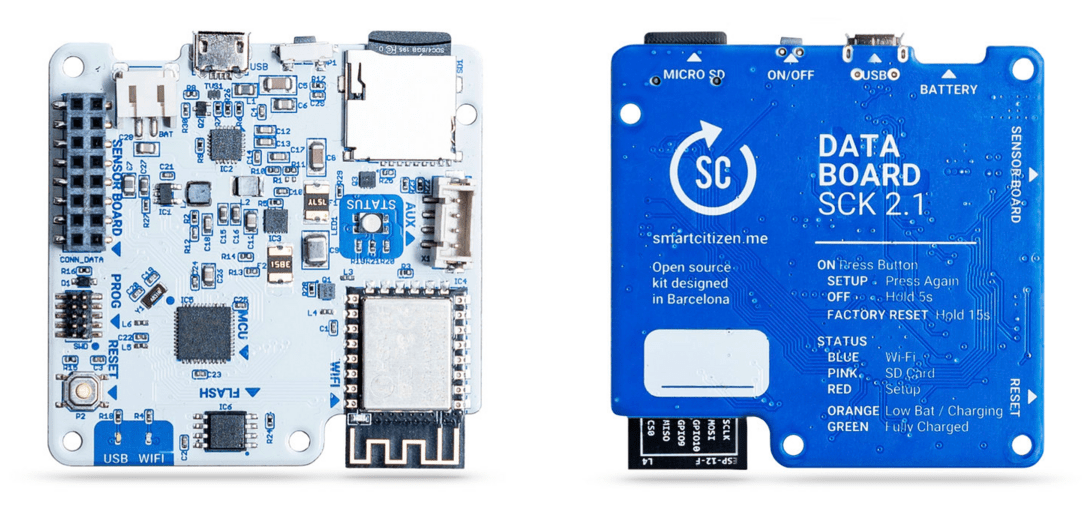
Smart Citizen Kit
With the help of the multi-sensor Smart Citizen Kit, anyone can monitor and share information about their surroundings, adding to a world wide network of open-source environmental data.
The Smart Citizen Kit was created with the intention of enabling people to actively contribute to the sustainability of their surroundings.
It’s a user-friendly tool kit for monitoring the environment, and can be used in schools and for citizen science projects, as well as being appropriate for advanced research projects.
The prototype was made using an Arduino board, and it included sensors to measure things like air quality, noise level, temperature, humidity, and other parameters.
The Smart Citizen data board is at the core of the production version of Smart Citizen Kit and the Smart Citizen Station. It’s powered by an ARM M0+ 32-bits 48Mhz SAMD21 that runs the firmware.
It combines the ARM M0 family’s low power consumption with the power of a 32-bits processor that has 32 KB of RAM and 256 KB of FLASH memory.
They needed a solution like this that provides enough program storage and memory space to support the kit’s many different sensors.
The data board uses the same chip found in the Arduino MKR series of boards, and the Arduino Zero.
Since inclusivity and ease of adaptation is at the core of the project, it’s a great benefit to be able to draw on the Arduino community that uses these same boards, and all the resources already out there for users.
The group also had to create a platform so that users could quickly upload, visualize, and interpret the data that their gadgets were collecting.
Thousands of people around the world have embraced the Smart Citizen Kit, as an easy way to collect and process environmental data.
The Touch Board by Bare Conductive
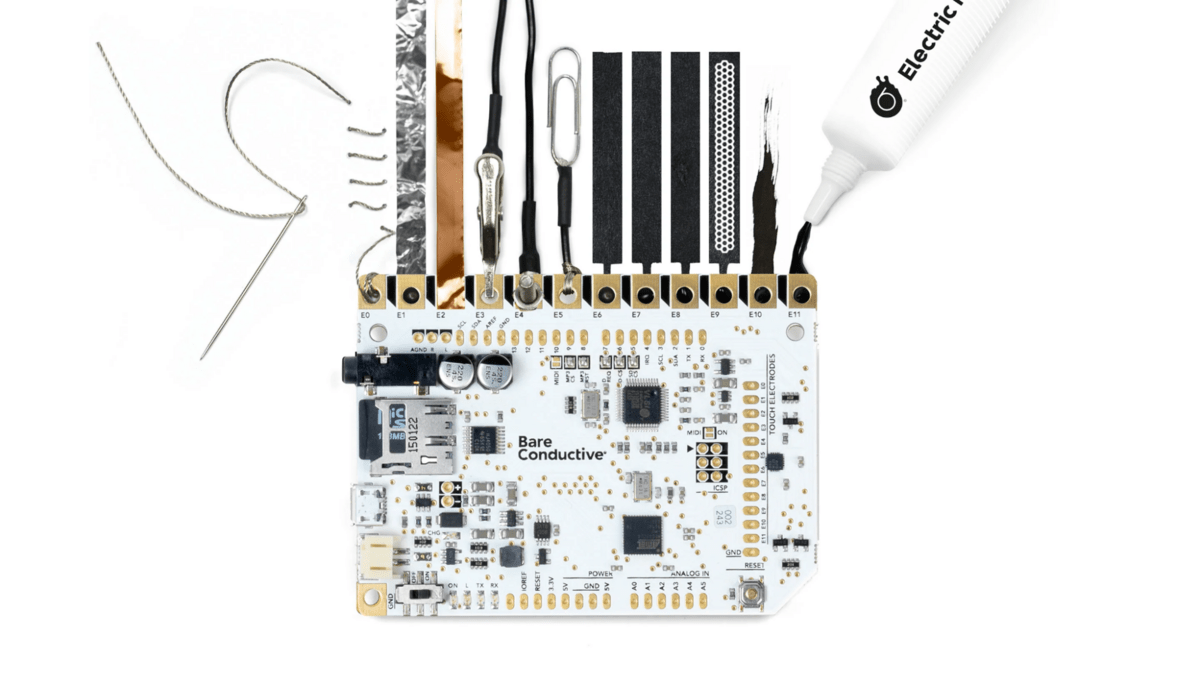
The Touch Board was created by the London-based business Bare Conductive as an Arduino-compatible tool that turns any conductive material into a touch-sensitive surface. Imagine a poster that plays music when you touch its paint, for example.
The possibility of employing conductive paint in conjunction with electronics to produce original interactive experiences served as the inspiration for the product concept.
During the prototyping phase, a big issue was constructing a small and user-friendly board that could be quickly combined with conductive materials and programmed using Arduino software.
The group had to make sure the board worked with different conductive materials without losing performance.
Following the prototype’s improvement and functional testing, Bare Conductive started a Kickstarter campaign that brought in more than $150,000.
With this financial boost, they were able to open distribution channels, engage with manufacturers, and purchase high-quality components.
The production version of Touch Board uses a microcontroller board based on the Arduino Leonardo, using the ATmega32U4.
It has a 3.5mm audio jack and sounds or music can be stored on the board via a microSD card.
The Touch Board is programmed using the Arduino IDE and a micro USB cable.
Because of the unique interactive features that the Touch Board offers, it has gained popularity among designers, artists, and educators.
A growing user base has developed as a result of its success, sharing cutting-edge ideas and applications.
The conductive inks and paints that work with the product provide a nice recurring revenue stream for the company.
KEYESTUDIO IOT Smart Home Kit
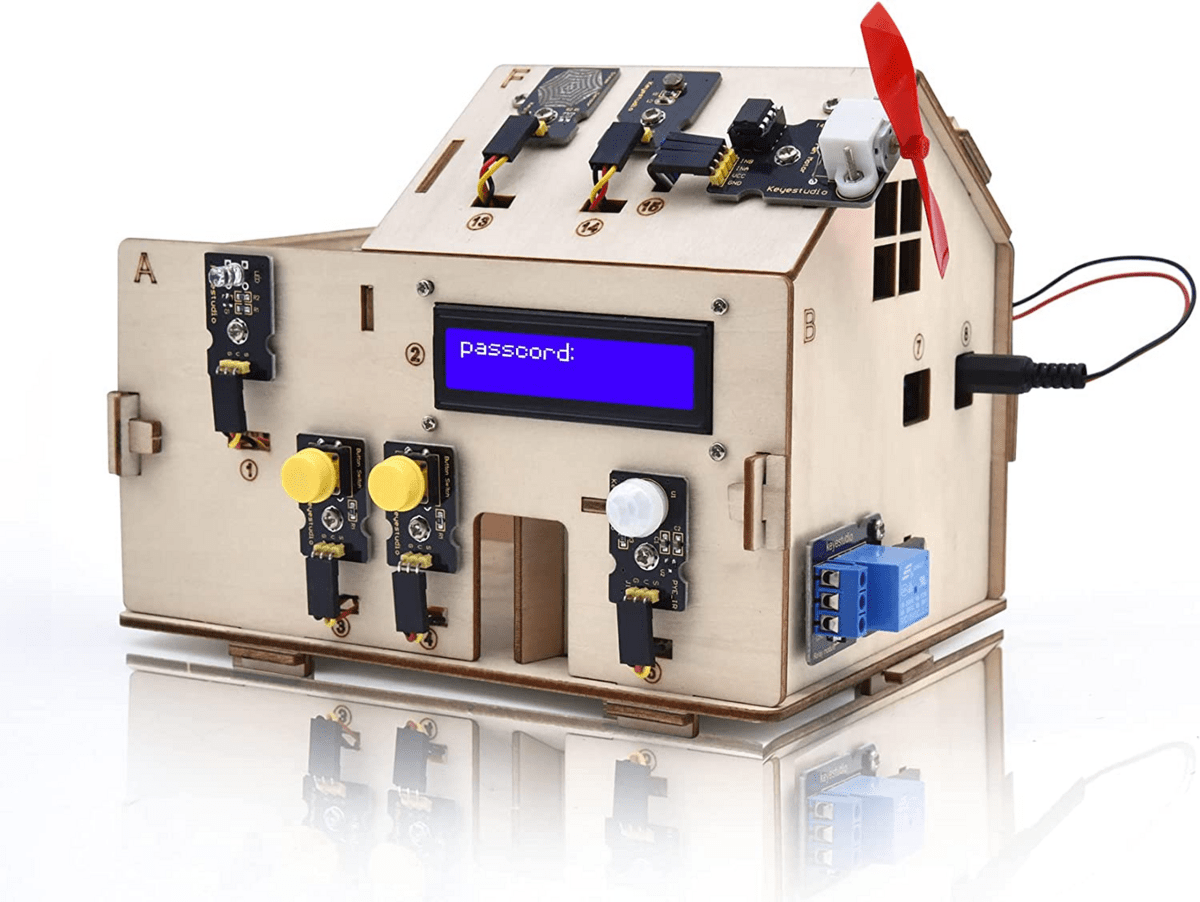
While these products started off using Arduino boards, like the Uno, they never graduated to a custom board after moving to larger scale production levels.
In fact, KEYESTUDIO built a whole line of products around specifically using Arduino chips, to control one of their robots for example.
The company’s “Smart Home Automation Kit” retails for around $65, and enables users to transform their homes into smart, automated environments, allowing for increased convenience and control over various household systems.
The Smart Home Automation Kit utilizes an Arduino microcontroller, there are various models to choose from, as the central brain of the system, that communicates with and manages the different components of the kit.
The kit typically includes several components and modules that can be interconnected and programmed using the Arduino. Temperature, humidity and motion sensors are some of the kit’s components.
Since KEYESTUDIO’s various products stay with the Arduino platform, users can leverage the Arduino libraries to program custom automation routines.
They can even be integrated with voice assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant for voice control.
Next you may enjoy these popular articles next:
– 5 Successful Products Powered by Raspberry Pi
– 5 Successful Products Powered by an ESP32 Wireless Microcontroller
– 5 Successful Hardware Startups That Were Bootstrapped
Written by Jessica Teel